Infections can cause a wide range of side effects, depending on the type of infection and the area of the body it affects. Infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. Below are some common side effects and the types of infections that might lead to them:
Common Side Effects of Infections:
- Fever: A common response to infections as the body attempts to fight off pathogens.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or weak due to the body’s immune system working overtime.
- Pain: Infections can cause pain, such as in the throat (pharyngitis), chest (pneumonia), or urinary tract (UTIs).
- Swelling and Redness: Often seen with bacterial infections, such as skin infections or abscesses.
- Cough and Sore Throat: Often associated with respiratory infections.
- Headache: Can occur with infections like flu, sinusitis, or meningitis.
- Digestive Issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal pain, common with gastrointestinal infections.
- Rashes: Some infections, such as measles, chickenpox, or viral exanthems, can cause skin rashes.
- Pus or Discharge: Sign of infection in wounds or mucous membranes.
- Chills and Sweats: Seen with many bacterial infections or viral illnesses like the flu.
- Shortness of Breath: May occur with respiratory infections or lung conditions like pneumonia or COVID-19.
- Organ Dysfunction: In severe cases, infections can damage organs, leading to conditions like sepsis, liver failure, or kidney problems.
Types of Infections:
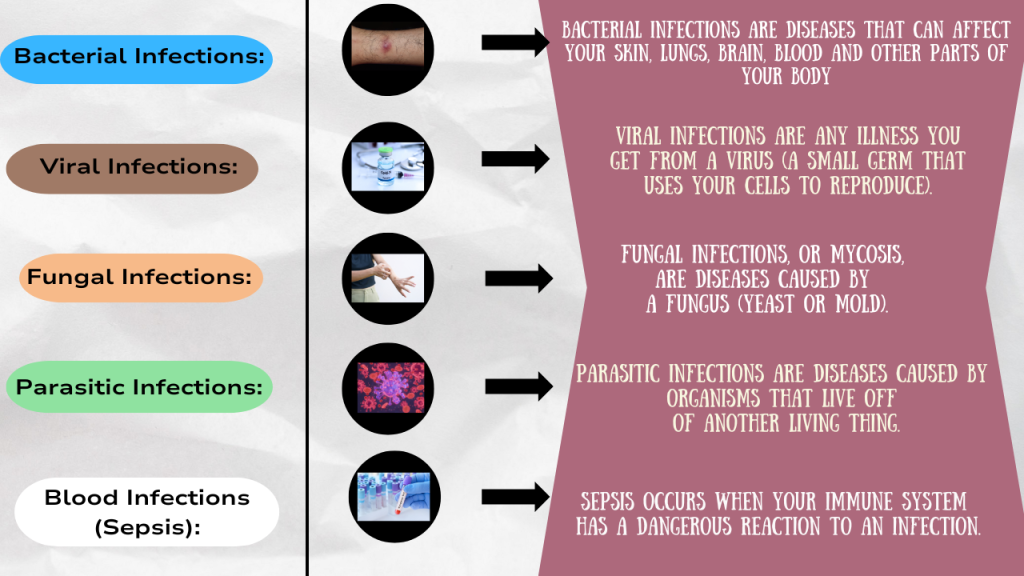
- Bacterial Infections:
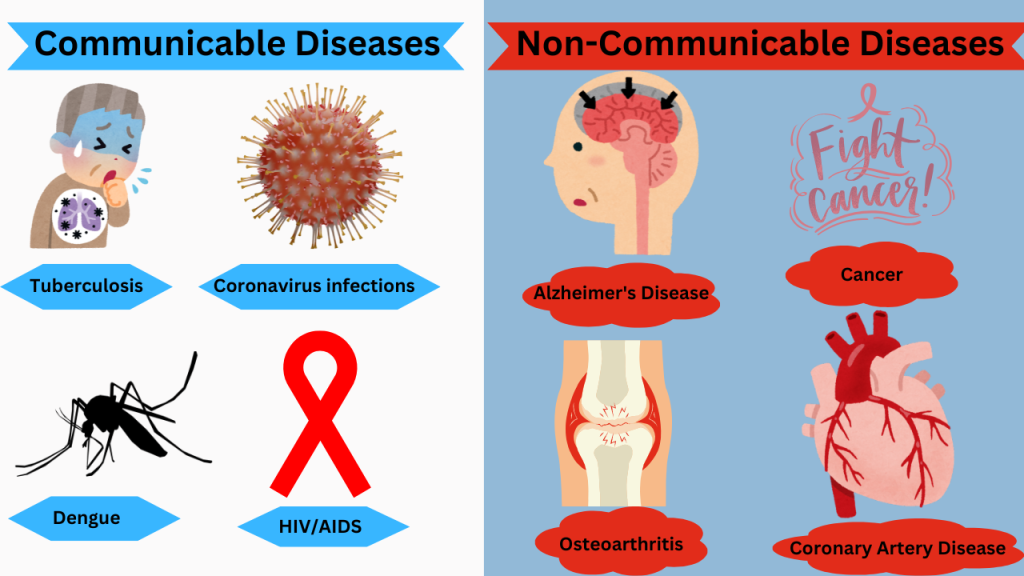
- Examples: Pneumonia, tuberculosis, urinary tract infections (UTIs), strep throat, bacterial skin infections (e.g., cellulitis).
- Side Effects: Can include fever, localized pain, swelling, and pus formation.
- Viral Infections:
- Examples: Common cold, flu (influenza), COVID-19, HIV, chickenpox, hepatitis, herpes simplex virus (HSV).
- Side Effects: Fever, fatigue, cough, sore throat, rash, joint pain, and more systemic symptoms like muscle aches.
- Fungal Infections:
- Examples: Athlete’s foot, candida infections (e.g., thrush), ringworm, aspergillosis.
- Side Effects: Itching, redness, scaling of the skin, rashes, pain, and sometimes systemic symptoms if the infection spreads.
- Parasitic Infections:
- Examples: Malaria, giardiasis, toxoplasmosis, trichomoniasis.
- Side Effects: Fever, fatigue, digestive symptoms, anemia, and sometimes neurological or eye issues, depending on the parasite.
- Protozoal Infections:
- Examples: Amoebic dysentery, malaria, toxoplasmosis.
- Side Effects: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight loss, and sometimes more serious effects on organs like the liver or brain.
- Mycobacterial Infections:
- Examples: Tuberculosis (TB), leprosy.
- Side Effects: Chronic cough, weight loss, night sweats, fever, and in some cases, damage to lungs and other organs.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs):
- Examples: Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, HPV, herpes simplex.
- Side Effects: Painful urination, discharge, sores, rashes, and systemic symptoms in advanced cases (e.g., HIV).
- Blood Infections (Sepsis):
- Cause: Can result from any untreated or severe infection, such as bacterial pneumonia or a UTI.
- Side Effects: Rapid heart rate, confusion, difficulty breathing, chills, and low blood pressure. Sepsis is a life-threatening condition.
Severe and Long-Term Effects:

- Organ Damage: Infections can cause permanent damage to organs (e.g., kidney failure from a severe UTI or liver damage from hepatitis).
- Chronic Fatigue: Some infections, like Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), can cause long-term fatigue.
- Autoimmune Responses: Certain infections can trigger autoimmune disorders, where the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues.
- Antibiotic Resistance: Overuse or misuse of antibiotics can cause bacterial infections to become resistant to treatment.
Infections can vary significantly in their effects depending on the pathogen, the individual’s immune response, and whether the infection is treated promptly. It’s important to seek medical attention when symptoms persist or worsen.


