The difference between junk food and home food lies in several key factors, including nutritional content, preparation methods, and overall health impact.
1. Nutritional Value:

- Junk Food: Typically high in calories, sugar, sodium, and unhealthy fats (like trans fats), while being low in nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Examples include fast food, chips, candy, soda, and packaged snacks.
- Home Food: Usually made with fresh ingredients and can be nutritious. It is easier to control the amount of added sugars, salt, and fats. Home-cooked meals often include more vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, making them more balanced.
2. Ingredients:

- Junk Food: Often contains artificial additives, preservatives, flavor enhancers (like MSG), and unhealthy oils to enhance taste, shelf life, and texture.
- Home Food: Made with whole foods like fresh vegetables, fruits, grains, lean meats, and natural herbs. There are fewer processed ingredients and preservatives.
3. Health Impact:
- Junk Food: Regular consumption of junk food can lead to weight gain, obesity, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and other chronic conditions due to its poor nutritional quality and high levels of unhealthy fats and sugars.
- Home Food: Home-cooked meals are generally better for your overall health because you can control the portion sizes, ingredients, and cooking methods. They can support healthy weight management and lower the risk of chronic diseases.

4. Preparation:
- Junk Food: Usually prepared quickly with little to no effort, often deep-fried, microwaved, or heated. It is designed for convenience and is often consumed on the go.
- Home Food: Requires time and effort to prepare and cook. Meals are often made from scratch, allowing for better control over cooking methods (e.g., grilling, baking, steaming), which can preserve nutrients and reduce excess fats.
5. Portion Sizes:
- Junk Food: Often comes in large portions or packaged sizes that encourage overeating, which can contribute to unhealthy eating habits.
- Home Food: Portions can be controlled based on personal needs and preferences. It is easier to prepare meals in appropriate serving sizes, which can help prevent overeating.
6. Cost:
- Junk Food: Sometimes cheaper in the short term, especially when purchased in bulk or in processed forms (e.g., chips, sugary drinks). However, the health costs of consuming junk food over time can outweigh the initial savings.
- Home Food: Can be more cost-effective in the long run, especially if you buy ingredients in bulk or prepare meals ahead of time. Home cooking allows for portion control, which may help reduce food waste.
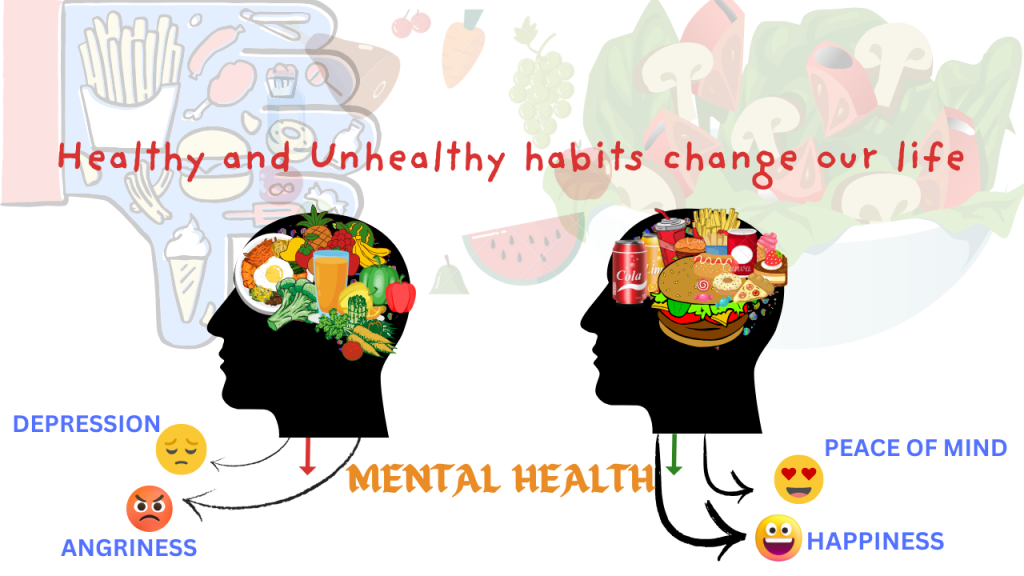
7. Emotional Satisfaction:
- Junk Food: Often designed to be addictive, with intense flavors and satisfying textures, which can trigger emotional responses like temporary pleasure or stress relief, but it may not provide long-lasting satiety.
- Home Food: While home-cooked meals may not offer the same immediate gratification, they provide sustained energy and can be more emotionally fulfilling, especially when shared with loved ones.
In summary, junk food is convenient, often unhealthy, and made with processed ingredients, whereas home food is typically healthier, made with fresh ingredients, and offers greater control over nutritional content and portion sizes.


